(Microsoft PowerPoint - 1.ve2.Hafta_0_Giri\376_Kavramlar ve
advertisement
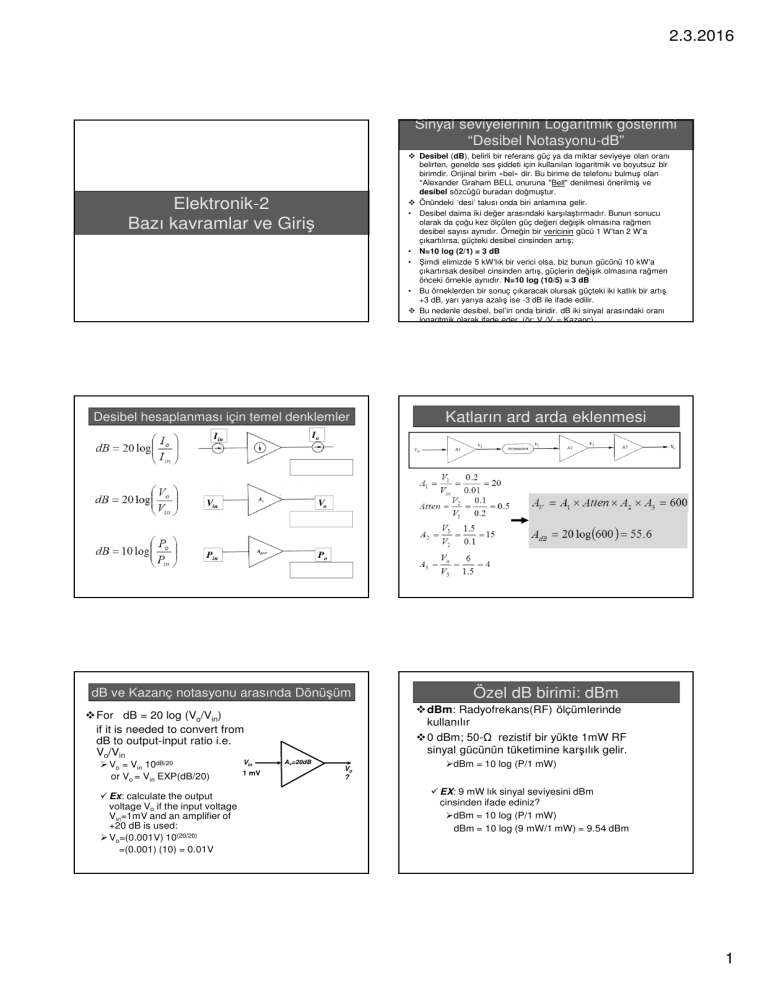
2.3.2016
Sinyal seviyelerinin Logaritmik gösterimi
“Desibel Notasyonu-dB”
Desibel (dB), belirli bir referans güç ya da miktar seviyeye olan oranı
belirten, genelde ses şiddeti için kullanılan logaritmik ve boyutsuz bir
birimdir. Orijinal birim «bel» dir. Bu birime de telefonu bulmuş olan
*Alexander Graham BELL onuruna "Bell" denilmesi önerilmiş ve
desibel sözcüğü buradan doğmuştur.
Önündeki ‘desi’ takısı onda biri anlamına gelir.
• Desibel daima iki değer arasındaki karşılaştırmadır. Bunun sonucu
olarak da çoğu kez ölçülen güç değeri değişik olmasına rağmen
desibel sayısı aynıdır. Örneğin bir vericinin gücü 1 W'tan 2 W'a
çıkartılırsa, güçteki desibel cinsinden artış;
• N=10 log (2/1) = 3 dB
• Şimdi elimizde 5 kW'lık bir verici olsa, biz bunun gücünü 10 kW'a
çıkartırsak desibel cinsinden artış, güçlerin değişik olmasına rağmen
önceki örnekle aynıdır. N=10 log (10/5) = 3 dB
• Bu örneklerden bir sonuç çıkaracak olursak güçteki iki katlık bir artış
+3 dB, yarı yarıya azalış ise -3 dB ile ifade edilir.
Bu nedenle desibel, bel’in onda biridir. dB iki sinyal arasındaki oranı
logaritmik olarak ifade eder. (ör: Vo/Vi = Kazanç)
Elektronik-2
Bazı kavramlar ve Giriş
Desibel hesaplanması için temel denklemler
Iin
Vin
Vo
Pin
Po
dB ve Kazanç notasyonu arasında Dönüşüm
For dB = 20 log (Vo/Vin)
if it is needed to convert from
dB to output-input ratio i.e.
Vo/Vin
Vo = Vin 10dB/20
or Vo = Vin EXP(dB/20)
Ex: calculate the output
voltage Vo if the input voltage
Vin=1mV and an amplifier of
+20 dB is used:
Vo=(0.001V) 10(20/20)
=(0.001) (10) = 0.01V
Katların ard arda eklenmesi
Io
Vin
1 mV
Özel dB birimi: dBm
dBm: Radyofrekans(RF) ölçümlerinde
kullanılır
0 dBm; 50-Ω rezistif bir yükte 1mW RF
sinyal gücünün tüketimine karşılık gelir.
Av=20dB
Vo
?
dBm = 10 log (P/1 mW)
EX: 9 mW lık sinyal seviyesini dBm
cinsinden ifade ediniz?
dBm = 10 log (P/1 mW)
dBm = 10 log (9 mW/1 mW) = 9.54 dBm
1
2.3.2016
dBm
Voltaj(gerilim)
dönüşümü
Voltajın dBm’e çevrilmesi :
Use the expression P=V2/R=V2/50 to find milliwatts, and then use the
equation of dBm
EX: 800 μV rms değerindeki sinyali dBm cinsinden ifade ediniz
P=V2/50
P=0.00000064 V / 50 Ω→p=0.0000128 mW
dBm = 10log(P/1mW)= -48.9
dBm’in voltaja çevrilmesi:
Find the power level represented by the dBm level, and then calculate
the voltage using 50 Ω as the load.
EX: what voltage exists across a 50- Ω resistive load when -6 dBm
is dissipated in the load?
P=(1 mW)(10dBm/10)
P =(1 mW)(10-6 dBm/10) =(1 mW)(10-0.6) =(1 mW)(0.25)=0.25 mW
If P=V2/50, then V = (50P)1/2 = 7.07(P1/2), V = (7.07)(P1/2) = (7.07)(0.251/2) = 3.54 mV
Bilimsel Notasyon
Bilimsel notasyonda bir sayının formu şu
şekildedir:
N X 10x {Unit}
N: Sayı
10: Taban
x: üs
Eğer mevcutsa, her zaman sonuçların BİRİMİni
yazınız
ORTALAMA
Birim as/üs katları
Symbol
Name
Multiplication
p
piko
1 x 10-12
n
nano
1 x 10-9
μ
Mikro
1 x 10-6
m
mili
1 x 10-3
k
Kilo
1 x 103
M
Mega
1 x 106
G
Giga
1 x 109
T
Tera
1 x 1012
Definition
Most typical value or most expected value in a collection
of numerical data
Different kinds of average
Mean: the sum of all values divided by the number (n) of
different values:
Median:
The middle value in the data set
Mode:
The most frequently occurring value in the data
set
Root-mean-square “rms”
Integrated Average
This average is applied
often in RC circuits
The output of the circuit ~
time average of the input
signal
EX: Comparing of AC sine wave
current with DC current level that
will produce the same amount of
heating in an electrical resistance.
V
V1
T
Volts
The area under the curve of
a time dependent function
divided by the segment of
the range over which the
average is taken
Used in electrical circuits and
certain technologies
0
t1
Time
t2 t
Definition of rms:
Vrms: is the rms value
T: is the time interval t1 to t2
V(t): is the time-varying voltage
function
Special case: the rms for sine
wave value of voltage is Vp/√2 or
0.707 Vp (Vp is the peak voltage)
2
2.3.2016
Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law: A voltage of 1V across a resistance
of 1Ω will cause a current of 1 A to flow. The
formula is
R = V / I
(where R = resistance in Ω, V = Voltage in V,
and I = current in A)
V = R * I
I = V / R
Reactance
The impedance (reactance) of a capacitor,
which varies inversely with frequency (as
frequency is increased, the reactance falls and
vice versa).
XC = 1 / (2 Π f C)
where Xc is capacitive reactance in Ohms, (Π pi) is 3.14159,
f is frequency in Hz, and C is capacitance in Farads.
Inductive reactance, being the reactance of an
inductor. This is proportional to frequency.
XL = 2 Π f L
where XL is inductive reactance in Ohms, and L is inductance
in Henrys
Frequency
Frequency
There are many different ways for the
calculations of the frequency, depending
on the combination of components.
The -3dB frequency for resistance and
capacitance (the most common in amplifier
design) is determined by
fo = 1 / (2 Π R C)
where fo is the -3dB frequency
When resistance and inductance are combined,
the formula is
fo = R / (2 Π L)
Power
The power in any form can be calculated by
many means:
P=V I
P = V2 / R
P = I2 R
Where:
P
is the power in [W]
V
is the voltage in [V]
I
is the current in [A]
Amplification Basics
Kuvvetlendirici=Amplifikatör=Yükselteç
The term "amplify" basically means to make stronger.
The strength of a signal (in terms of voltage) is
referred to as amplitude
Types of amplification
There are three kinds of amplifications: Two major
types, and the third type is derived from the another
two :
Voltage Amplifier - an amp that boosts the
voltage of an input signal
Current Amplifier - an amp that boosts the
current of a signal
Power Amplifier - the combination of the above
two amplifiers
3
2.3.2016
Voltage and current amplifier
Voltage amplifier:
In the case of a voltage amplifier, a small input
voltage will be increased
so that for example a 10mV (0.01V) input signal might
be amplified so that the output is 1 Volt.
This represents a "gain" of 100 - the output voltage is
100 times as great as the input voltage. This is called
the voltage gain of the amplifier.
Current amplifier:
In the case of a current amplifier, a small input
current will be increased.
an input current of 10mA (0.01A) might be amplified
to give an output of 1A
Again, this is a gain of 100, and is the current gain of
the amplifier.
Types of Amplifiers
1.
Vacuum Valve-Lamba
2.
Transistor-Transistör
3.
Operational amplifier-İşlemsel Kuvvetlendirici
2. Transistor
Bipolar junction transistor
(BJT) are two diodes
joined with a very thin
common region
A small electrical input can
be amplified by transistor
A simple one-transistor
amplifier with positive
and negative supplies
Power Amplifier
Power gain
If we now combine the two amplifiers, then
calculate the input power and the output power, we
will measure the power gain:
P=VxI
(where I = current, note that the symbol changes in a
formula)
The input and output power can be now calculated:
Pin = 0.01 x 0.01
(0.01V and 0.01A, or 10mV and 10mA)
Pin = 100 µW
Pout = 1 x 1
(1V and 1A)
Pout = 1W
The power gain is therefore 10,000, which is the
voltage gain multiplied by the current gain.
1. Vacuum Valve
In electronics, a vacuum
tube or (outside North
America) thermionic
valve or just valve, is a
device generally used to
amplify, switch or
otherwise modify, a
signal by controlling the
movement of electrons in
an evacuated space.
Bioelectric Amplifier
Is the amplifier that used to process bio-potentials
The gain may be low, medium or high (X10, X100,
X10000)
It is usually ac coupled.
DC-coupling is required where the input signal are
clearly dc or change very slowly (0.05 Hz)
Exceptional for EX.: ECG signal should be AC
coupled despite of the component as low as 0.05
Hz to overcome electrode offset potential from
electrode-skin connection
The high-frequency response is the frequency at
which the gain drops 3dB below its midfrequency
value (for ECG form 0.05 to 100 Hz)
4
2.3.2016
Bioelectric Amplifier
Low gain amp: gain factor bw X1 and X10
Unity gain (X1) used for isolation, buffering and
possibly impedance transformation bw signal
source and readout device.
Used for relatively high-amplitude bioelectric
events (EX: action potential)
Medium gain amp: gain factor bw X10 and X1000
(EX: ECG, Muscles potentials, …)
High gain or low-level signal amp: gain factor over
X10000 to as high as X1000000 (EX: EEG)
Biyoelektrik kuvvetlendirici
Önemli parametreler:
Gürültü(Noise): normally is the thermal noise
generated in resistances and semiconductors
devices.
Kayma (Drift): change in output signal voltage caused
by change in operating temperature.
Yüksek giriş empedansı(High input impedance): 107
to 1012 Ω and it should be at least an order of
magnitude high than the source impedance.
Tümdevre olması(Integrated circuit (IC)): operational
amplifier is well suited as bioelectric amp because of
its properties.
Operational amplifiers
Osilatörlerin Türleri
• RC tipi lineer Osilatörler (Sinusoidal-Geri beslemeli)
– Wien Köprü Osilatörü
– Faz kaymalı Osilatör
• LC tipi Osilatörler (Sinusoidal-Geribeslemeli)
– Colpitts Osilatör
– Clapp Osilatör
– Hartley Osilatör
– Kristal kontrollü Osilatör
• Sinusoidal olmayan osilatörler
- Kare dalga Osilatör
- Üçgen dalga osilatör
Ref:06103104HKN
EE3110 Oscillator
28
Osilatörler
Osilatörlerin Uygulamaları
Osilasyon: Düzenli ve tekrarlı bir şekilde
ortalama bir değer civarında genlikte
dalgalanmalara denir.
Osilatör: Osilasyon üreten devreye denir.
Karakteristikleri: dalga şekli, frekans, genlik,
distorsiyon, kararlılık
• Oscillators are used to generate signals, e.g.
– Used as a local oscillator to transform the RF
signals to IF signals in a receiver;
– Used to generate RF carrier in a transmitter
– Used to generate clocks in digital systems;
– Used as sweep circuits in TV sets and CRO.
29
30
5
2.3.2016
Integrant of Linear Oscillators
Basic Linear Oscillator
and
For sinusoidal input is connected
“Linear” because the output is approximately sinusoidal
If Vs = 0, the only way that Vo can be nonzero
is that loop gain Aβ=1 which implies that
A linear oscillator contains:
- a frequency selection feedback network
- an amplifier to maintain the loop gain at unity
(Barkhausen Criterion)
31
Wien Köprü Osilatör-İSPAT
32
Faz Kaymalı Osilatör-ÖDEV
33
34
Konular:
1.1 İşlemsel (operasyonel) yükseltecin (opamp) tanıtılması
1.2 Farksal (differential) Yükselteç
1.3 Opamp Karakteristikleri
Amaçlar:
BMM 214 Elektronik-2
2. HAFTA
İşlemsel Yükselteçler
Operational Amplifier
Bu bölümü bitirdiğinizde aşağıda belirtilen konular hakkında ayrıntılı bilgiye
sahip olacaksınız.
Operasyonel yükseltecin tanıtımı ve sembolü,
İdeal opamp özellikleri
Pratik opamp özellikleri ve 741 tipi tümdevre opamp’ın tanıtılması ve
terminal bağlantıları
Opamp’ın temel yapısı ve blok olarak gösterimi
Opamp Karakteristikleri
6
2.3.2016
Opamp Sembolü ve Terminalleri
Elektronik piyasasında çok çeşitli amaçlar için üretilmiş binlerce
tip opamp vardır. Tümdevreler genellikle bu kodlarla anılırlar.
Şekil-1.3’de genelde pek çok üreticinin uyduğu kodlama
sistemi iki ayrı tümdevre üzerinde kodlamada uygulanan kurallar
ile birlikte gösterilmiştir.
Kodlama genellikle 3 gruba ayrılarak yapılır.
Op-amp
It has two inputs: the inverting input (-) and the
non-inverting input (+), and one output.
It has usually two supplies (±Vss) but it can work
with one.
-Vss
Inverting
input
Non-inverting
Output
+
input
+Vss
Symbol of op-amplifier
7
2.3.2016
What is inside the Op-amp?
The Op Amp is basically three amplifiers or stages.
The input differential stage; the gain stage, and the output
stage.
741 Op-Amp Schematic
current mirror
voltage
level
shifter
differential amplifier
Op-Amp Characteristics
current mirror
current mirror
output
stage
high-gain amplifier
Ideal Op-Amp Characteristics
• Open-loop gain G is typically over 9000
• But closed-loop gain is much smaller
• Rin is very large (MΩ or larger)
• Rout is small (75Ω or smaller)
• Effective output impedance in closed loop is very small
Real vs. Ideal Op-amp
Parameter
• Open-loop gain G is infinite
• Rin is infinite
• Zero input current
• Rout is zero
Ideal Op Amp Typical Op Amp
Open-loop voltage gain A
∞
105 – 109
Common mode voltage gain
0
10-5
Frequency response f
∞
1- 20 MHz
Input impedance Zin
∞
106 Ω (bipolar)
109–1012 Ω (FET)
Output impedance Zout
0
100 – 1000 Ω
8
2.3.2016
Önemli Parametreler
Kaynak Voltajı (Supply
Voltage (±Vss)):
The maximum voltage (positive
and negative) that can be safely
used to feed the op-amp.
Farksal giriş voltajı:
This is the maximum voltage that
can be applied across the + and
– inputs.
Giriş voltajı
The maximum input voltage that
can be simultaneously applied
between both input and ground
also referred to as the commonmode voltage.
In general, the maximum voltage
is equal to the supply voltage.
Important Parameters
Sürüklenme hızı (Slew Rate (SR)):
Is the time rate of change of the
output voltage with the op-amp circuit
having a voltage gain of unity (1.0).
SR = max rate at which amplifier
output can change in V/µs
SR defines the Op-amps ability to
handle varying signals.
SR defines how fast the amplifier is.
Önemli Parametreler
Giriş dengesizlik Voltajı (Input Offset Voltage (Voff)):
This is the voltage that must be applied to one of the input
pins to give a zero output voltage. Remember, for an ideal
op-amp, output offset voltage is zero!
Giriş kutuplama akımı(IB):
This is the average of the currents flowing into both inputs.
Ideally, the two input bias currents are equal.
Açık çevrim voltaj kazancı(Ao):
The output to input voltage ratio of the op-amp without
external feedback.
Ortak mod zayıflatma Oranı
(Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR)):
A measure of the ability of the op-amp' to reject signals
that are simultaneously present at both inputs.
It is the ratio of the common-mode input voltage to the
generated output voltage, usually expressed in (dB).
Examples
Giriş dengesizlik
voltajı ayarlanması
(Input offset voltage
adjustment:)
Kaynak Voltajı
(Supply Voltage)
If op-amp is driven at rates > SR
(given in the spec. sheet) signal clipping & distortion.
Bir opamp’ın çıkışından alınabilecek maksimum çıkış gerilimi, besleme
geriliminden birkaç volt daha küçüktür. Bu durum opamp’ın iç yapısından ve enerji
tüketiminden kaynaklanır. Opamp çıkışında elde edilen işaretin maksimum
değerlerine doyum (saturation) gerilimi denir. ±VSAT olarak ifade edilir.
Örneğin besleme gerilimi ±12V olan bir opamp’ta doyum gerilimleri negatif işaretler
için 2V, pozitif işaretler için ise 1V daha azdır.
Yani opamp çıkışından pozitif değerler için maksimum +11V,
negatif değerler için ise maksimum -10V civarında bir gerilim alınabilir.
9
2.3.2016
Opamp çıkışından alınan işaretin polaritesi eviren ve evirmeyen
girişler arasındaki gerilimin farkına bağlıdır. Opamp’ın girişlerindeki
gerilim farkına fark gerilimi denir ve Vd ile tanımlanır.
Opamp; hem ac, hem de dc işaretleri kuvvetlendirmede kullanılan bir
devre elamanıdır. Bu özelliği dikkate alınarak opamp girişindeki
gerilim farkı;
Bir opamp’ın açık çevrim gerilim kazancı (AOL) teorik olarak
sonsuzdur. Pratikte ise oldukça yüksek bir değerdir.Bu durumda
opamp’ın eviren (V1) ve evirmeyen (V2) girişlerine uygulanan
işaretler;
V2>V1 ise fark gerilimi Vd pozitif olacak, opamp çıkışı +VSAT
değerini alacaktır.
V2<V1 ise fark gerilimi Vd negatif olacak, opamp çıkışı -VSAT
değerini alacaktır.
Op-Amp Saturation
• As mentioned
earlier, the
maximum output
value is the
supply voltage,
positive and
negative.
• The gain (G) is the
slope between
saturation points.
Vout
Vs+
Vin
Vs-
Pratikde çıkış gerilimi V0; iki sinyalin farkına (VD) ve ortak mod sinyaline
(VC) bağımlıdır. Bu değerler aşağıdaki gibi formüle edilirler;
Eğer girişte ortak mod sinyali yok ise (olması istenmez) VC = 0 dır.
Bu durumda çıkış sinyali;
Vo =VD ⋅AD
Devredeki amplifikasyon katsayısı ise bu durum da;
Formülde ki VC değeri ortak mod sinyalidir. Ortak Mod sinyali
VC, farksal yükselteci ideal durumdan uzaklaştırır. İyi
düzenlenmiş bir farksal yükselteçte ortak mod sinyalinin yok
edilmesi gerekir.
İki giriş için ortak mod sinyali (VC) ölçülebilir. Bu durum da
VD =0 yapılırsa, ortak mod kazancı
Kaliteli bir diferansiyel yükselteçte, diferansiyel kazanç
(AD ) büyük, Ortak mod kazancı (AD ) ise küçük olmalıdır.
10
2.3.2016
Diferansiyel yükseltecin kalitesini tayin etmek amacı ile bu iki kazanç arasındaki
orana bakılır. Bu oran ortak mod eleme oranı (Common-mode rejection ratio:
C.M.R.R) olarak isimlendirilir. Aşağıdaki şekilde ifade edilir.
Örnek
Bir op-amp`ın Ad = 800 ve AC= 0.1 dir. Op-amp`ın CMRR değeri kaç dB
dir?
Çözüm
CMRR(dB) = 20 log[Ad \ AC]
CMRR(dB) = 20 log [800 \0.1]
CMRR(dB) = 20 log 8000
CMRR(dB) = 78 dB
Örnek
Aşağıda verilen op-amp`lardan hangisini tercih edersiniz?
Op-amp 1
CMRR = 90 dB
Op-amp 2
CMRR = 85 dB
Op-amp 3
CMRR = 120 dB
Çözüm
☺DC işaretlerin işlenmesinde hata oluşturan faktörler nelerdir?
Her zaman için CMRR değeri yüksek olan op-amp daha iyidir. Bu sebepden
dolayı op-amp 3 tercih edilir.
☺ AC işaretlerin işlenmesinde hata oluşturan faktörler nelerdir?
Opamp’ta oluşan gerilim dengesizliğinin nasıl sıfırlanacağı
bazı opamp tipleri için şekil-1.13’de verilmiştir.
Verilen yöntemler denenmiş en uygun yöntemlerdir.
Örnek olarak verilen opamp devrelerinde çıkış hata gerilimi
bir ayarlı direnç vasıtası ile sıfırlanmaktadır.
İdeal bir opamp’ın giriş uçları topraklandığında çıkış gerilimi
Vo=0V olmalıdır. Pratikte ise opamp çıkışından 0V yerine, değeri
bir kaç mikrovolt ile milivolt mertebesinde değişen
hata gerilimleri alınabilir.
11
2.3.2016
İdeal durumda opamplarda giriş gerilimi Vi=0V olduğunda çıkış
gerilimi Vo=0V olmalıdır.
Pek çok uygulamada kutuplama akımları ihmal edilebilir.
12
2.3.2016
Örnek
Çözüm
İdeal bir op amp için, Ri yüksek, Ro düşük, A OL yüksek, CMRR yüksek
ve SR hızlı olmalıdır. Bu kriterler göz önünde bulunursa op-amp I ideal
karakteristiklere çok yakın olandır.
Op-Amp Eşdeğeri ile Bir
Örnek Çözümü-Chapter 5
(sf. 169)
ÖDEV- (sf. 169)5.1
13