LİNEER CEBİR GİRİŞ DERSİ BİLGİ FORMU
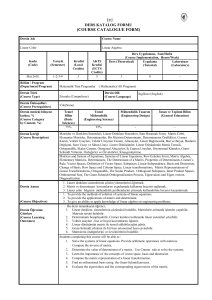
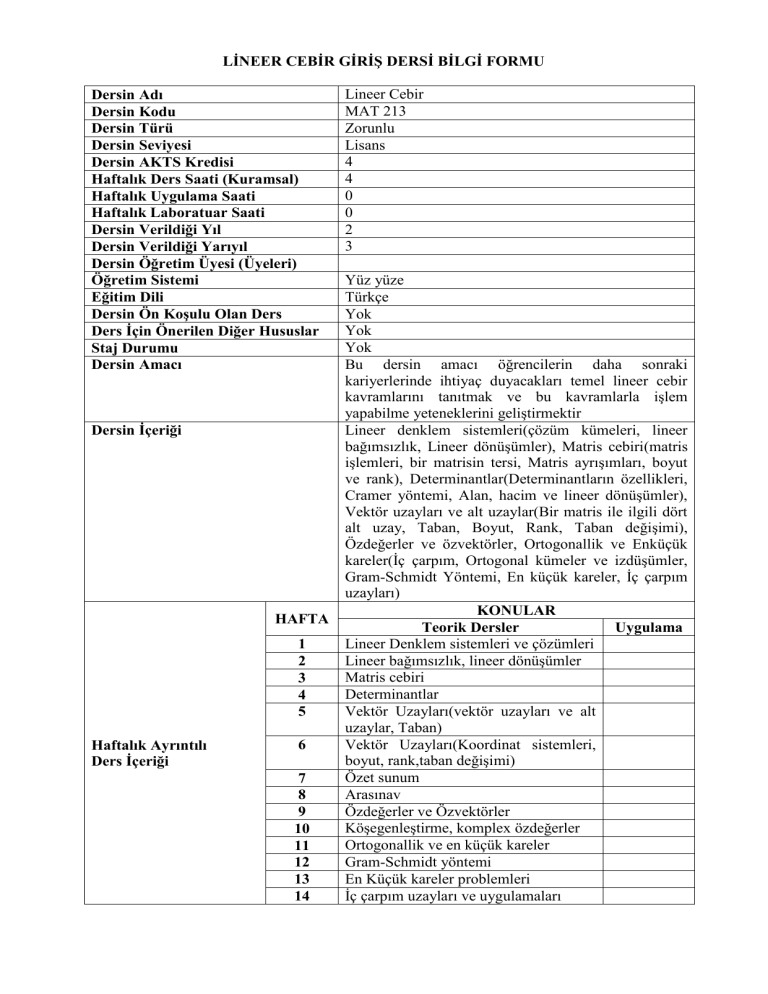
Dersin Adı
Dersin Kodu
Dersin Türü
Dersin Seviyesi
Dersin AKTS Kredisi
Haftalık Ders Saati (Kuramsal)
Haftalık Uygulama Saati
Haftalık Laboratuar Saati
Dersin Verildiği Yıl
Dersin Verildiği Yarıyıl
Dersin Öğretim Üyesi (Üyeleri)
Öğretim Sistemi
Eğitim Dili
Dersin Ön Koşulu Olan Ders
Ders İçin Önerilen Diğer Hususlar
Staj Durumu
Dersin Amacı
Dersin İçeriği
HAFTA
1
2
3
4
5
Haftalık Ayrıntılı
Ders İçeriği
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
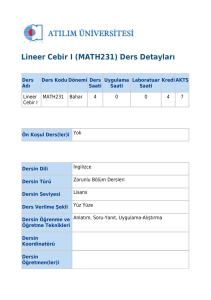
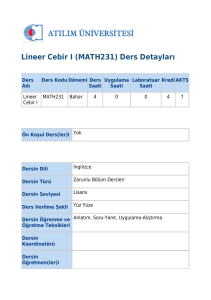
Lineer Cebir
MAT 213
Zorunlu
Lisans
4
4
0
0
2
3
Yüz yüze
Türkçe
Yok
Yok
Yok
Bu dersin amacı öğrencilerin daha sonraki
kariyerlerinde ihtiyaç duyacakları temel lineer cebir
kavramlarını tanıtmak ve bu kavramlarla işlem
yapabilme yeteneklerini geliştirmektir
Lineer denklem sistemleri(çözüm kümeleri, lineer
bağımsızlık, Lineer dönüşümler), Matris cebiri(matris
işlemleri, bir matrisin tersi, Matris ayrışımları, boyut
ve rank), Determinantlar(Determinantların özellikleri,
Cramer yöntemi, Alan, hacim ve lineer dönüşümler),
Vektör uzayları ve alt uzaylar(Bir matris ile ilgili dört
alt uzay, Taban, Boyut, Rank, Taban değişimi),
Özdeğerler ve özvektörler, Ortogonallik ve Enküçük
kareler(İç çarpım, Ortogonal kümeler ve izdüşümler,
Gram-Schmidt Yöntemi, En küçük kareler, İç çarpım
uzayları)
KONULAR
Teorik Dersler
Uygulama
Lineer Denklem sistemleri ve çözümleri
Lineer bağımsızlık, lineer dönüşümler
Matris cebiri
Determinantlar
Vektör Uzayları(vektör uzayları ve alt
uzaylar, Taban)
Vektör Uzayları(Koordinat sistemleri,
boyut, rank,taban değişimi)
Özet sunum
Arasınav
Özdeğerler ve Özvektörler
Köşegenleştirme, komplex özdeğerler
Ortogonallik ve en küçük kareler
Gram-Schmidt yöntemi
En Küçük kareler problemleri
İç çarpım uzayları ve uygulamaları
Öğrenme Çıktıları
Özet sunum
15
Dönem sonu sınavı
16
ÖÇ - 1 : Lineer denklem sistemlerini analiz edebilir ve mümkünse
çözüm veya çözümlerini belirleyebilirler
ÖÇ - 2 : Çözüm mevcut olmadığı durumda en iyi yakın çözümü
belirleyebilirler
ÖÇ - 3 : Vektör uzayı ve alt uzaylar konusunda gerekli bilgiye
sahip olur ve ilgili problemleri çözme yeteneklerini geliştirmiş
olurlar
Ders Kitabı/
Malzemesi/
Önerilen
Kaynaklar
ÖÇ - 4 : Özellikle analitik yaklaşım yöntemlerinde aranan en iyi
çözümün ortogonal izdüşüm yardımıyla belirlenebileceğini
gözlemlemiş olurlar
DERS KİTABI:
Lay, David C., 2003, Linear Algebra and its applications, Addison
Wesley
Hacısalihoğlu, Hilmi, 2000 Lineer Cebir, Hacısalihoğlu Yayıncılık
DERS ARAÇLARI: Ders notları
DEĞERLENDİRME
Yarıyıl (Yıl) İçi Etkinlikleri
Ara sınav
TOPLAM
Yarıyıl (Yıl) İçi Etkinliklerinin Başarı
Notuna Katkısı
Yarıyıl (Yıl) Sonu Sınavının Başarı
Notuna Katkısı
Sayısı
1
1
Yarıyıl (Yıl) Notuna Katkısı %
40
40
60
TOPLAM
100
Dersin Öğrenme, Öğretme ve Değerlendirme Etkinlikleri Çerçevesinde
İş Yükünün Hesaplanması
Etkinlikler
Sayısı
Süresi
Toplam İş Yükü
(Saat)
(Saat)
Yüz yüze eğitim
14
3
42
Arasınav için hazırlık
7
4
28
Arasınav
1
2
2
Dönem sonu sınavı için hazırlık
7
6
42
Dönem sonu sınavı
1
2
2
Derse Ön Hazırlık
4
2
8
TOPLAM İŞ YÜKÜ (Saat) = 124
DERSİN AKTS KREDİSİ= Toplam İş Yükü(saat)/(30saat/AKTS)= 4
Program ve Öğrenme Çıktıları İlişkisi
Ders
Öğrenme
Çıktıları
Program Çıktıları
PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ PÇ
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 10 11 12
ÖÇ 1
4
3
2
3
3
3
2
2
3
4
3
2
4
3
3
4
2
2
4
2
4
3
3
3
4
3
3
2
3
4
4
2
3
2
3
4
3
3
3
3
4
2
4
3
4
2
4
2
3
4
2
3
2
3
4
3
ÖÇ 2
ÖÇ 3
ÖÇ 4
ÖÇ 5
ÖÇ 6
ÖÇ 7
ÖÇ 8
ÖÇ 9
ÖÇ 10
ÖÇ 11
ÖÇ 12
*Katkı Düzeyi: 1 Çok düşük
2 Düşük
3 Orta
4 Yüksek
5 Çok yüksek
LINEAR ALGEBRA INDIVIDUAL COURSE DESCRIPTION
Course Unit Title
Course Unit Code
Type of Course Unit
Level of Course Unit
Number of ECTS Credits Allocated
Theoretical (hour/week)
Practice (hour/week)
Laboratory (hour/week)
Year of Study
Semester when the course
unit is delivered
Name of Lecturer (s)
Mode of Delivery
Language of Instruction
Prerequisities and corequisities
Recommended Optional
Programme Components
Work Placement(s)
Objectives of the Course
Course Contents
Weekly Detailed
Course Contents
Linear Algebra
MAT 213
Compulsory
Undergraduate
4
4
0
0
2
3
Face to face
Turkish
None
None
None
This course introduces fundamental concepts of linear
algebra which are indispensable in all branches of
basic sciences
Linear equations in linear algebra(systems of
equations, row reduction and echelon forms, Linear
independence, Linear transformations), Matrix
algebra(Matrix operations, inverse of a matrix, Matrix
factorizations),
Determinants(Properties
of
determinants, Cramer's rule, Volume and linear
transformations), Vector spaces and Subspaces(Four
fundamental subspaces related to a matrix,
Dimensions, Rank, Change of basis), Eigenvalues and
eigenvectors, Ortogonality and least squares(Inner
product, Orthogonal sets and projections, GramSchmidt Process, least square problems, inner product
spaces
TOPICS
WEEKS
Theoretical Courses
Application
Systems of linear equations and their
1
solution sets
Linear
independence,
Linear
2
transformations
Matrix algebra
3
Determinants
4
Vector spaces (vector spaces and
5
subspaces, bases)
Vector spaces (Coordinat systems,
6
dimension, rank, change of bases)
A summary
7
Mid-term exam
8
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors
Diagonalization, complex eigenvalues
Orthogonality and least squares
The Gram-Schmidt Process
Least-Squares problems
Inner product spaces and their
applications
A summary
15
End-of-term exam
16
LO - 1 : Analyse linear systems and determine their solution or
solutions, if possible
9
10
11
12
13
14
Learning Outcomes
LO - 2 : Determine the best approximate solution in case the
system fails to have a solution
LO - 3 : Have knowlege and develop skills to handle problems on
vector spaces and their subspaces
Textbook/ Material/
Recommended
Readings
LO - 4 : Observe that the best approximate solution that one seeks
in approximation problems is obtained thorough the orthogonal
projections
Course Book:
Lay, David C., 2003, Linear Algebra and its applications, Addison
Wesley
Hacısalihoğlu, Hilmi, 2000 Lineer Cebir, Hacısalihoğlu Yayıncılık
Course Materials: Course notes
ASSESSMENT
Semester (Year) Interior
Activities
Laboratory test reports
Laboratory practical exam
Homework
Supervision
TOTAL
Semester (year) Grades of Domestic
Contribution Activities
Semester (year) of the Final Exam grade
Contribution
Number
Semester (year) Note the
%
Contribution to
1
1
40
40
60
TOTAL
Course Learning, Teaching and Assessment Activities in the
Framework Calculation of the workload
Number
Duration
Activities
Week
(hour)
Lectures (face to face teaching)
14
3
Own study for first mid-term exam
7
4
100
Total workload
(hour)
42
28
Mid-term exam
Own study for final exam
End-of-term exam
Study For The Course
1
2
7
6
1
2
4
2
TOTAL WORKLOAD (hour) = 124
AKTS CREDIT COURSE= Total Work Load(hour)/(30 hours/AKTS)= 4
2
42
2
8
Contribution of Learning Outcomes to Programme Outcomes
Programme Outcomes
Learning
Outcomes PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 11 12
LO 1
4
3
2
3
3
3
2
3
4
3
2
4
3
4
2
2
4
2
3
3
3
4
3
3
3
4
4
2
3
2
4
3
3
3
3
4
4
3
4
2
4
2
4
2
3
2
3
4
LO 2
LO 3
LO 4
LO 5
LO 6
LO 7
LO 8
LO 9
LO 10
LO 11
LO 12
*Contribution Level: 1 Very Low
2 Low
3 Medium
4 High
5 Very High