Name:
Spring 2011
11 June 2011
ME-210 Applied Math for ME
Std ID:
Final Examination
Grade:
Closed book and notes
Show all your calculation steps. No calculators.
Use the back side of the same sheet to continue solving a problem.
Duration: 130 minutes
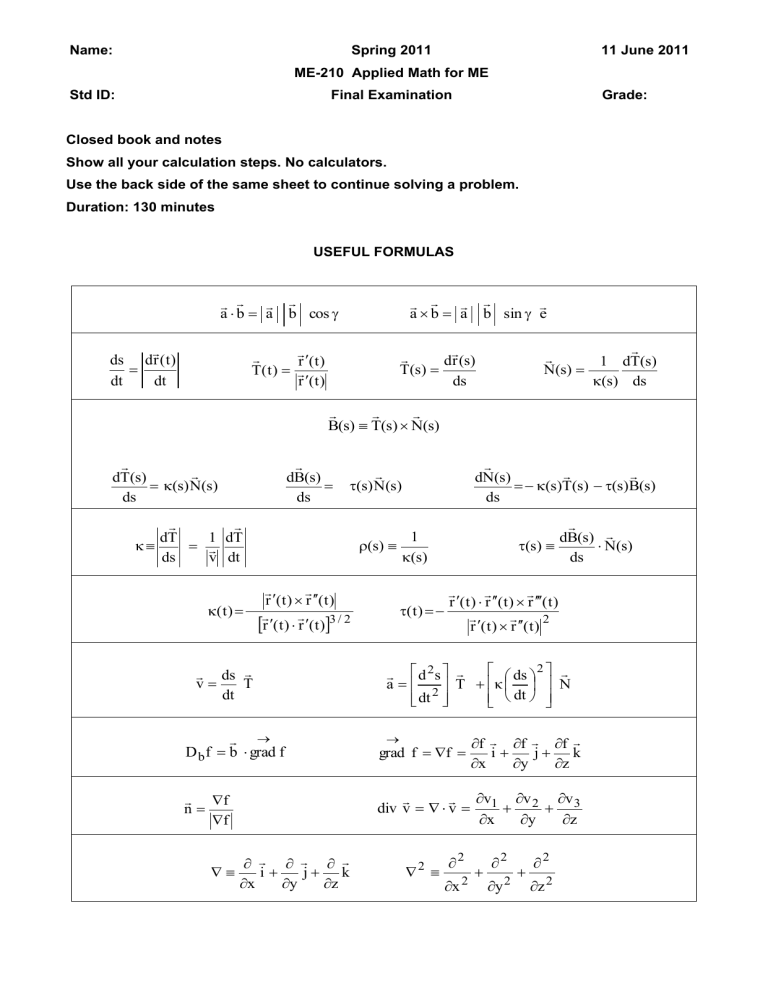
USEFUL FORMULAS
ab a
ds d r ( t )
dt
dt
ab a
b cos
b sin e
1 dT(s)
N(s)
(s) ds
d r (s)
T(s)
ds
r ( t )
T( t )
r ( t )
B(s) T(s) N(s)
dT(s)
(s) N(s)
ds
dB(s)
ds
dN(s)
(s)T(s) (s)B(s)
ds
(s) N(s)
dT
1 dT
ds
v dt
r ( t ) r ( t )
( t )
r (t ) r (t )3 / 2
ds
v
T
dt
dB(s)
(s)
N(s)
ds
1
(s)
(s)
r ( t ) r ( t ) r ( t )
( t )
2
r ( t ) r ( t )
ds 2
d 2s
κ N
a
T
dt
dt 2
D b f b grad f
grad f f
f
n
f
v
v
v
div v v 1 2 3
x
y
z
i
j k
x
y
z
2
2
x 2
f f f
i
j k
x
y
z
2
y 2
2
z 2
v v
v
v v
v
curl v v 3 2 i 1 3 j 2 1 k
z z
x x
y
y
div (v) 0
t
curl (f ) 0
n
If [C] [A][B]
det([A])
n
(1)
j k
k 1
c jk a jib ik
then
i 1
n
det([A]) (1) j k a jk M jk
a jk M jk
j 1
where j 1, 2, ..., or n
where k 1, 2, ..., or n
[A] - 1 =
xi = Di / D
Adj[A]
det[A]
Adj[A] = [C i j ] T
e i = cos + i sin
(cos + i sin) n = cos(n) + i sin(n)
[A] [x] = [x]
2k
2k
z n r n cos
i sin
,k = 0,1,2, … ,n -1
n
n
1
ez = e(x
1
+ iy )
= ex eiy
ln(z) = ln |z| + i arg(z)
cosh(z) = ( e z + e – z ) / 2
sinh(z) = ( e z – e – z ) / 2
cos(z) = ( e i z + e – i z ) / 2
sin(z) = ( e i z – e – i z ) / 2i
df
f (z o z) f (z o )
lim
dz z zo z0
z
w = f(z) = f(x + iy) = u(x,y) + i v(x,y)
ux = vy
df
u x i vx
dz z zo
u y = -v x
∯( ⃗ ̂)
∬( ⃗ ̂)
∭(
∬[ ⃗ ( (
∬⃗ ̂
∫ ⃗ ( ⃗)
) (
∬(
⃗
⃗)
)) ⃗⃗]
) (
⃗) ̂
∫ ⃗ ( ⃗( ))
⃗
z z0
QUESTION 1 (20 points)
Find all the possible solutions for the following system of equations using Gauss Elimination and back
substitution:
2w 3x 2y 7
3w y z 7
2x y z 1
SOLUTION
Matrix representation of the system of equations:
w
2 3 2 0 7
3 0 1 1 x 7
y
0 2 1 1 1
z
The augmented matrix:
2 3 2 0
3 0 1 1
0 2 1 1
7
7
1
Gauss elimination:
1
2 * 2 2 3 1
3
2 3 2 0
0 9 4 2
0 2 1 1
7
7
1
2 3 2 0
0 9 4 2
0 0
1 5
7 1
7 2
5 3 * 9 3 2 2
Back substitution:
y - 5 z = 5 => y = 5 + 5 z
-9 x + 4 y - 2 z = -9 x + 20 + 20 z - 2 z = -9 x + 20 + 18 z = -7 => x = 3 + 2 z
2 w + 3 x - 2 y = 2 w + 9 + 6 z - 10 - 10 z = 2 w - 1 - 4 z = 7 => w = 4 + 2 z
4 2
5 5
All possible solutions: + z , where z is arbitrary.
3 2
0 1
QUESTION 2 (20 points)
Find the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of
1 0 0
M 1 0 1 .
1 1 0
Check your results by multiplying [M] with the eigenvectors you found.
SOLUTION
Characteristic polynomial:
1 0
0
M I 1 1 1 2 1 0
1
1
Eigenvalues: 1 2 1 0 1,2 1 , 3 1.
Eigenvectors corresponding to eigenvalue 1,2 1 :
1 1 0 0 x1
0
1 1 x 2 0
1 1 1 x3 3 0
x1 x2 1 x3 1
M 1I 1
c1 c2
1
1
c2
0
1
x1 1 x2 1 x3 1 0
x 1 c1 c1 1 c2 0 , where c1 and c2 are arbitrary.
1 0 0 c1+c2 c1+c2
Check: 1 0 -1 c1 = c1
1 -1 0 c2 c2
Eigenvectors corresponding to eigenvalue 3 1 :
1 1 0 0 x1
0
x13 0
M 1I 1 1 1 x2 0
x2 3 x3 3
1 1 1 x3 3 0
0
0
x 3 c3 c3 1 , where c3 is arbitrary.
c3
1
1 0 0 0 0
Check: 1 0 -1 c3 = -c3 =
1 -1 0 c3 -c3
0
c
3
c3
QUESTION 3 (10+10 points)
a) Evaluate
sin i
and express the result in Cartesian form, i.e., find the real and imaginary parts.
2i
b) Find (all possible values for) z when zz z 1 i .
SOLUTION
sin π - i ei π-i - e-i π-i
e1+iπ - e-1-iπ
e1 cos π + i sin π - e-1 cos -π + i sin-π
=
=
=
2+i
2 i 2 + i
2 -1 + i 2
2 -1 + i 2
a)
=
- e + e-1
- e + e-1
-1 - i 2
e - e-1 1 + i 2 e2 - 1
e2 - 1
=
=
=
+
i
-1 + i 2 -1 - i 2
2 -1 + i 2
2
2 1 + 22
10 e
5e
b) Let z = x + iy z z + z = x + i y x - i y + x + i y = x2 + y2 + x + i y = 1 + i .
Real part: x2 y2 x 1
2
x 1 x 1
Imaginary part: y 1
x2 x x x 1 0
x 0 or x 1
Roots: z1 i , z2 1 i
QUESTION 4 (10×2 points)
Let f x,y,z = x2 - y z and v x,y,z v1 x,y,z i v2 x,y,z j v3 x,y,z k x2 i y z j . State whether the
following expressions make sense and evaluate them if possible:
a) f
b) f
d) v
c) f
e) v f) v
g) f
h) f
i) v
SOLUTION
a) f
f
f
f
i
j
k 2 x i z j y k.
x
y
z
b) f : Divergence of a scalar function is not defined.
c) f : Curl of a scalar function is not defined.
d) v : Gradient of a vector function is not defined.
e) v
v1 v2 v3 2 f
f
x y z 0 2 x z .
x y z x
y
z
v v
v v
v v
f) v 3 2 i 1 3 j 2 1 k .
z x
y z
x y
0 yz i x2 0 j yz x2 k y i .
z
x
y
z
y
x
j
g) f i
x
y
z
k 2 x i z j y k 2x z y 2 .
x
y
z
h) f 0 , because curl of the gradient of a scalar function is always zero.
i) v : v 2 x z is a scalar function and curl of a scalar function is not defined.
j
j) v i
y
z
x
k y i y 0 .
x
j) v
QUESTION 5 (20 points)
Evaluate
1 x dA , where the surface S is the cylinder x
2
+ y2 = 1 between z = 0 and z = 1 + x.
S
Hint: Let x = cos(θ), and find the parametric representation of the surface S as r ,z
dA
r r
dz d
z
SOLUTION
Let x cos y 1 x2 sin . Then, a parametrization for S is: r ,z cos i sin j z k .
r
r
sin i cos j ,
k
z
1 x dA
S
2 1 cos
0
2
0
i
j
k
r r
sin cos 0 cos i sin j cos2 sin2 1
z
0
0
1
2
2
1 cos r r dz d 1 cos 2 d 1 2cos cos2 d
z
0
0
2
cos2 1
sin2
3
0 1 2 cos 2 d 2 2 sin 4 0 3
